




Operation Dominic
1962 - Christmas Island, Johnston Island, Central Pacific
Last changed 27 June 2021
The Soviet Union had abrogated the 34 month old de facto nuclear testing moratorium on 1 September 1961 by initiating an unprecedented series of atmospheric nuclear tests. The initial U.S. response was to commence its own test series (Operation Nougat) two weeks later. Nougat was an underground series however, restricted to very low yield devices.
Numerous atmospheric tests, many at high yield, were of course on the drawing board at the weapons labs, some carried over from planning for previous test series. Official U.S. action on convening its own atmospheric series did not begin until 10 October 1961 when President Kennedy approved planning for one. Final approval was given on 2 March 1962, 7 weeks in advance of the first planned test.
Dominic included 36 tests. The majority of the tests (29 airdrops) were weapons development tests, intended to evaluate advanced designs that the labs had been cooking up during the years of the moratorium and before. Five rocket-launched tests were conducted to gather further weapons effects data on high-altitude phenomena. Two tests of operational weapon systems were conducted - the Polaris submarine launched ballistic missile and the ASROC anti-submarine rocket.
Conducted as part of Operation Dominic was a series of high altitude tests known as Operation Fishbowl. These tests were Thor missile launched warheads detonated at very high altitudes (30-248 miles) to evaluate the destructive mechanisms and effects of high yield explosions against ballistic missile RVs. Several test failures occurred with missiles being destroyed in flight by range safety officers when electronics failed (Bluegill), when rocket motors malfunctioned (Starfish and Bluegill Prime), or when the missile veered out of control (Bluegill Double Prime). The Bluegill Prime test was particularly disastrous since the missile was blown up while still on the launch pad, requiring complete reconstruction of the demolished and plutonium contaminated Thor launch facility.
|
| Test: | Adobe |
|---|
| Time: | 15:45 25 April 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop, 2,900 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 190 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 15.4 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 44 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 409 |
|---|
Adobe was a free fall airburst that was a successful LASL verification test of the XW-50X1-Y2 warhead in a Mk-39 Mod-1 Type 3 drop case. The device was similar to those tested in Aztec, Kingfish, and Bluegill Triple Prime. The W-50 warhead was eventually deployed in three yields: Y1 (60 kt), Y2 (200 kt), and the Y3 (400 kt) and deployed on the Nike Zeus SAM (surface-to-air missile), and the Pershing surface-surface ballistic missile. The mushroom cloud rose to about 60,000 ft.
| Test: | Aztec |
|---|
| Time: | 16:01 27 April 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 10 Mi. S of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop, 2,610 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 410 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 15.4 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 44 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 409 |
|---|
This was a generally successful LASL of the the XW-50X1-Y3 in a Mk-39 Mod-1 Type 3 drop case. It was the highest yield variant of the W-50 warhead (used on the Nike Zeus and Pershing missiles), giving a yield-to-weight ratio of 2.21 kt/kg. This device used a spherical secondary stage. The device was similar to those tested in Adobe, Kingfish, and Bluegill Triple Prime. The yield was slightly lower than expected. The mushroom cloud rose to about 60,000 ft.
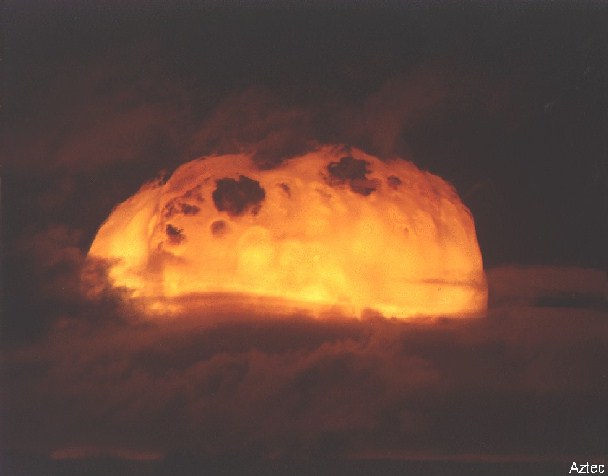 Dominic Aztec (34 K)
Dominic Aztec (34 K)
| Test: | Arkansas |
|---|
| Time: | 18:00.00.16 27 April 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop, 5,030 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 1090 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 17.36 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 47.3 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 600 |
|---|
This test was the first parachute-retarded device to be dropped at Christmas Island, it missed its intended air zero point by 600 ft. The aim point was over a raft moored off the southern end of Christmas Island.
Arkansas was a highly successful LRL test of the XW-56X2 (Fife-I) warhead for the Minuteman missile. This warhead was derived from the breakthrough LRL W-47 warhead developed for the Polaris missile. The characteristics of the two warheads are generally similar although the W-56 kept the same general yield (usually given as 1.2 Mt) as the high yield W-47Y2 variant, while trimming 133 pounds of the weight. This test used a Fife secondary stage. This test demonstrated a yield-to-weight ratio 4.00 kt/kg (remarkably close to the effective practical limit of 6 kt/kg for such a light weight device). The test device included a mockup war reserve firing set. This was similar to the devices (also W-56s) fired in Swanee and Bluestone. The mushroom cloud rose to about 60,000 ft.
About 1000 W-56s were eventually produced for the Minuteman I and II missiles. Some 450 remained in service until the Minuteman II was finally retired in the 1990s. The last W-56 was retired sometime between October 1992 and March 1993.
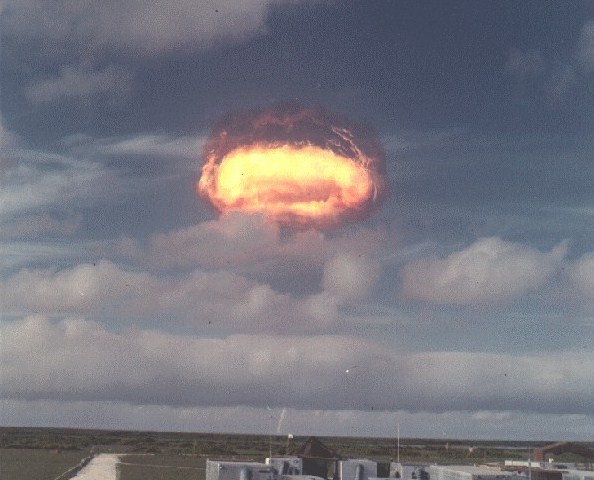 Dominic Arkansas (66 K)
Dominic Arkansas (66 K)
| Test: | Questa |
|---|
| Time: | 18:01 2 May 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 15 Mi. S of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 5,230 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 670 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 15.75 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 47.8 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 552 |
|---|
This was an LASL test of the XW-59 warhead in a Mk-39 Mod-1 Type 3 drop case. The W-59 was a development of the LASL J-21 warhead design and was a competitor with the LRL W-56 to arm the Minuteman I missile. It was also intended for the Skybolt air-launched (B-52 dropped) ballistic missile (this development effort halted on 21 December 1962 when the Skybolt program was cancelled). The device was similar to those tested in Alma, Rinconada, and Sunset. The yield (expected to be 1 Mt) was considerably lower than expected (the full yield was later achieved in Sunset). The yield-to-weight ratio of 2.68 kt/kg was still quite respectable. The mushroom cloud rose to 62,000 ft. with a base height of 35,000 ft.
In the end both the W-56 and W-59 were produced for the Minuteman I, about 150 of the later being produced between June 1962 and July 1963. Due in part to its somewhat higher yield, the W-56 was selected for use on the follow-on Minuteman II so the W-59 was retired from service with the Minuteman I system; all were retired between December 1964 and June 1969.
| Test: | Frigate Bird |
|---|
| Time: | 23:30 6 May 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 4 deg 50 min N, 149 deg 25 min W; 500 nm ENE of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | SLBM Airburst; 11,000 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 600 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 18 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 46.6 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 717 |
|---|
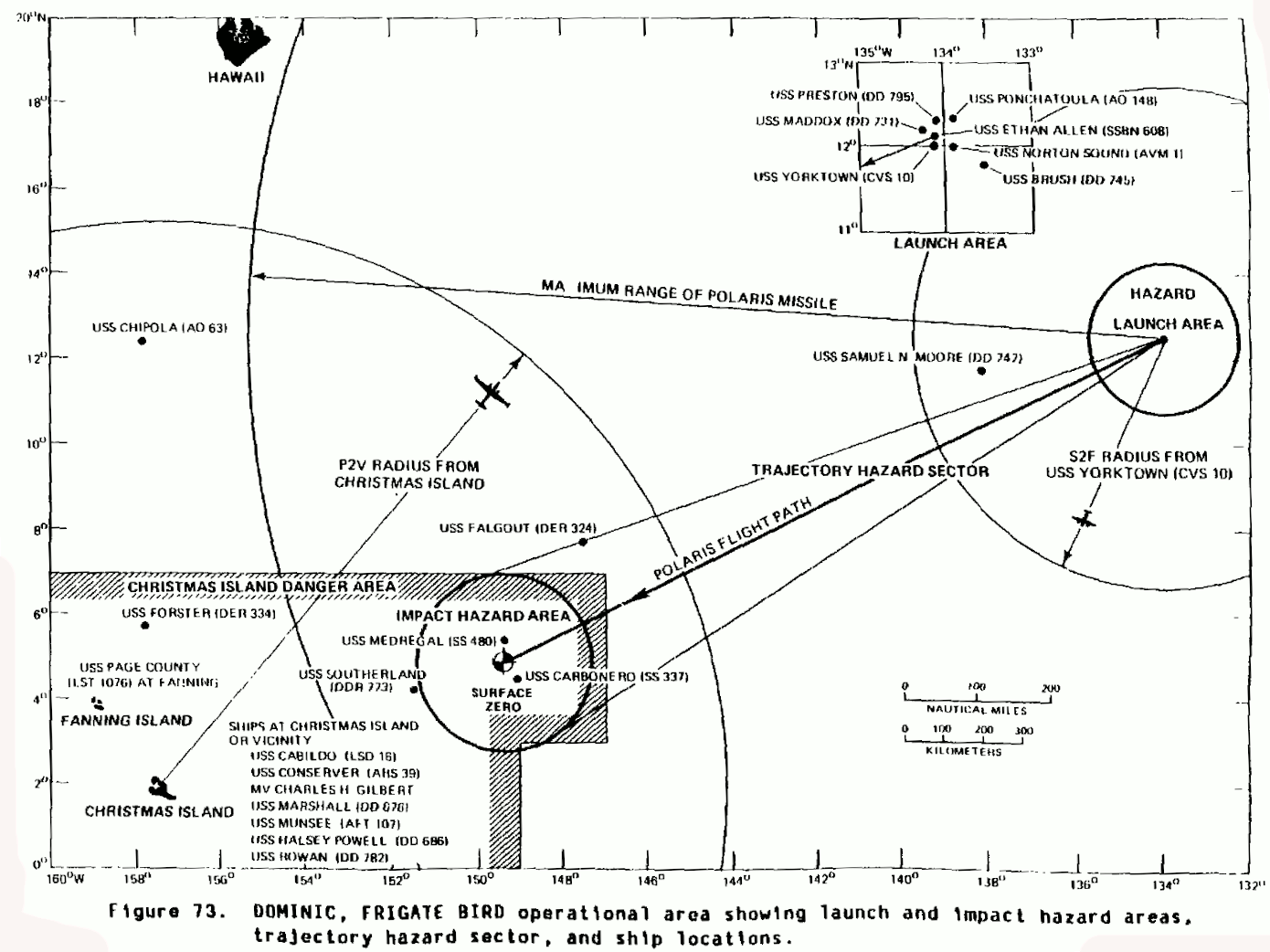
Frigate Bird was the only US test of an operational ballistic missile with a live warhead. This test involved firing a Polaris A1 missile from a ballistic missile submarine. The missile was launched by the USS Ethan Allen (SSBN-608) at 13:18 (local) from a position 1500 nm east-northeast of Christmas Island. The re-entry vehicle (RV) and warhead flew 1020 nm downrange toward Christmas Island before re-entering the atmosphere 12.5 minutes later, and detonating in an airburst at 11,000 feet. The system tested was a combination of a Polaris A1 SLBM, and a W-47Y1 warhead in a Mk-1 RV. The Mk-1 RV had a beryllium heat-sink heat shield, and with the 717 lb warhead had a gross weight of 900 lb. The missile/RV demonstrated an accuracy on the order of 2200 yards. This warhead had a yield-to-weight ratio of 1.84 kt/kg, but the higher yield Y2 variant tested in Dominic Harlem doubled the yield and nearly doubled tht YTW ratio to 3.61 kt/kg.
The image of the Frigate Bird mushroom cloud was taken through the periscope of the USS Carbonero (SS-337) 480 nm ENE of Christmas Island. The Carbonero (along with the USS Medregal, SS-480) was within 30 miles of the burst point.
| Test: | Yukon |
|---|
| Time: | 18:01 8 May 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 10 Mi. S of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 2,880 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 100 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 11.57 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 28.06 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | ? |
|---|
LRL parachute retarded test of the Calliope II device. This was an experimental shot, the first of a planned family of light weight, high-fusion/low-fission devices which were intended to increase the yield-to-weight ratio of ICBM warheads. The device was similar to those tested in Muskegon, Chetco, Nougat Arikaree, Hudson, Codsaw, and Hoosic. The yield was slightly higher than expected, the mushroom cloud rose to 57,000 ft.
 Dominic Yukon (44 K)
Dominic Yukon (44 K)
 Dominic Yukon (48 K, 360x460)
Dominic Yukon (48 K, 360x460)
| Test: | Mesilla |
|---|
| Time: | 17:01 9 May 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 10 Mi. S of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 2,450 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 100 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 16.5 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 26.4 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | ? |
|---|
Free-fall airdrop of the LASL Zippo-I device in a Mk-15 Mod 0 Type 3 drop case. Aimpoint was a target raft, missed the air zero point by 700 feet. This was an advanced concepts test for both primary and secondary designs. The yield was considerably lower than expected. Device was similar to that tested in Dulce.
| Test: | Muskegon |
|---|
| Time: | 15:37 11 May 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 10 Mi. S of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 2,995 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 50 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 11.57 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 26.96 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | ? |
|---|
LRL parachute retarded test of the Calliope IV device in Mk-36 drop case, missed the air zero point by 1000 feet. Advanced concepts test of lightweight low fission device. Similar to that tested in Chetco and Yukon. The yield was slightly lower than expected.
| Test: | Swordfish |
|---|
| Time: | 20:02 11 May 1962 (GMT)
13:02 11 May 1962 (local) |
|---|
| Location: | 400 nm W San Diego |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | Underwater; -650 Feet (Rocket Launched Depth Bomb) |
|---|
| Yield: | <20 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 13.75 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 25.3 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 160 |
|---|
This was the fifth and last U.S. underwater test. It was a DOD sponsored full scale test of the ASROC anti-submarine rocket weapon system. The ASROC used the LASL developed W-44 warhead (similar to that tested in Nougat Chena), which had a nominal yield of 10 kt. This shot had a number of objectives:
- It was a weapons effects test to evaluate how it would affect U.S. ships, submarines, and sonar systems in the area (a target array of four destroyers and a surfaced submarine were positioned at distances between 2200 and 4600 yards from surface zero);
- It was a safety test to evaluate the radiation hazard to the launching vessel;
- It was a proof firing of the ASROC by a regular Navy crew under simulated wartime conditions.
The ASROC was fired from the destroyer USS Agerholm (DD-826) at a target raft 4348 yards away. The rocket missed its sub-surface zero point by 20 yards and exploded 40 seconds later at a depth of 650 feet in water that was 17,140 feet deep.
 Dominic Swordfish launch (26 K)
Dominic Swordfish launch (26 K)
The spray dome from the detonation was 3000 feet across, and rose to 2100 feet in 16 seconds. The detonation left a huge circle of foam-covered radioactive water. Within two days it had broken up into small patches and spread out for 5 to 8 miles. In the picture below the Agerholm is in the foreground.
 Dominic Swordfish spray dome (25 K)
Dominic Swordfish spray dome (25 K)
 Dominic Swordfish spray dome dispersing(28 K)
Dominic Swordfish spray dome dispersing(28 K)
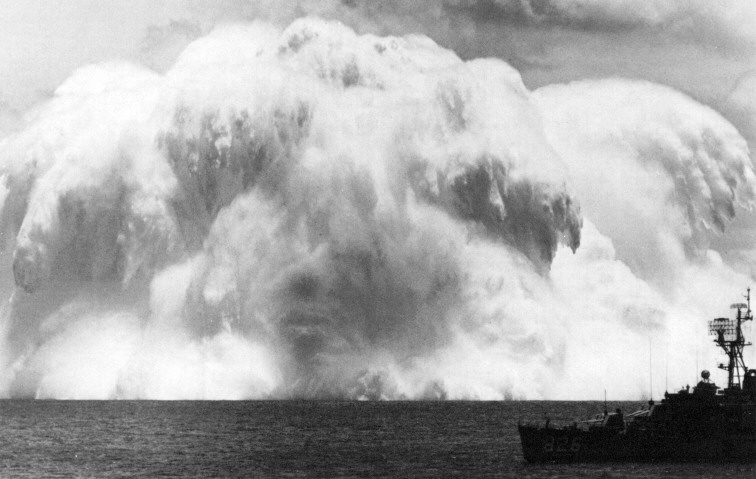 Swordfish spray dome dispersing further(80 K)
Swordfish spray dome dispersing further(80 K)
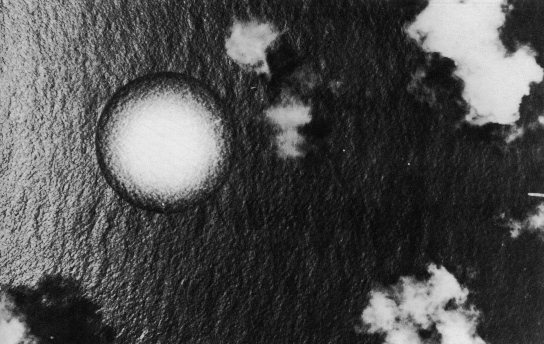 Swordfish spray dome from above (53 K)
Swordfish spray dome from above (53 K)
| Test: | Encino |
|---|
| Time: | 17:02 12 May 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 5,510 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 500 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 18 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 149.5 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 2060 |
|---|
This free-fall drop tested the LASL-designed XW-43Y5 warhead. The Mk-43 was a strategic bomb deployed in 5 yield variants (from 70 kt up to 1 Mt). This was a verification test of a reduced yield variant of the device fired in the HT-I Elder shot (880 kt). The purpose was to establish a normalization or reference point for future high yield designs. The bomb fell 1000 ft. from its air zero point. The mushroom cloud rose to 62,500 feet.
| Test: | Swanee |
|---|
| Time: | 15:21 14 May 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 10 Mi. S of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 2,940 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 97 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 17.13 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 38 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 506 |
|---|
This was a parachute retarded LRL XW-56 warhead dropped in a Mk-36 drop case. This was a highly experimental weapons development test to collect hydrodynamic and neutronic data on a "clean" weapon design to serve as a prototype of an anti-ballistic missile (ABM) warhead. The device was similar to the Arkansas and Bluestone tests (see Arkansas for more information about the W-56 warhead). The mushroom cloud rose to 55,000 feet.
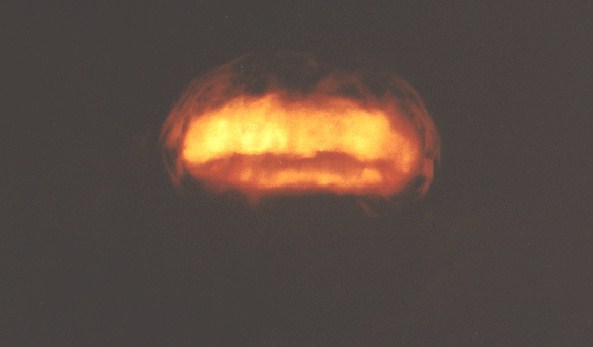 Dominic Swanee (22 K)
Dominic Swanee (22 K)
| Test: | Chetco |
|---|
| Time: | 15:36 19 May 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 10 Mi. S of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 6,905 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 73 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 11.57 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 28.06 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | ? |
|---|
This was a parachute retarded LRL Calliope I device in a Mk 36 drop case. This was an advanced concepts test of a light weight device. Device was similar to that tested in Muskegon and Yukon. The yield close to the predicted value. This drop missed its air zero point by only 200 feet, the official report stated that this test resulted in "the finest diagnostic data to date in this series".
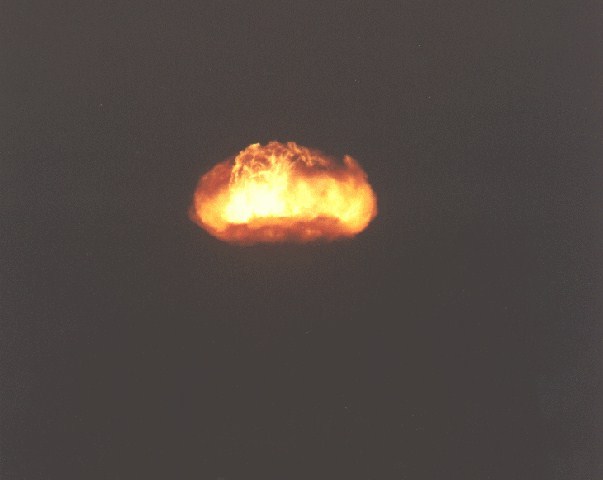 Dominic Chetco (29 K)
Dominic Chetco (29 K)
| Test: | Tanana |
|---|
| Time: | 16:08 25 May 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 10 Mi. S of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 9,030 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 2.6 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 19.62 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 37.45 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 153.57 |
|---|
This was a parachute retarded LRL Calliope III device in a Mk 36 drop case. The secondary failed to fire, resulting in a fizzle (the first of the Dominic series). Described as a "radical" advanced concepts test. Mushroom rose only to 23,000 feet.
| Test: | Nambe |
|---|
| Time: | 17:02 27 May 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 7,140 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 43 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 11.87 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 31.58 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | ? |
|---|
LASL free-fall test using a Zippo-II device in a Mk 15 Mod 0 Type 3 drop case. This was an advanced concepts test using a "unique" design. The yield was lower than expected. The cloud topped 61,000 feet. Good weather conditions permitted excellent test measurements.
 Dominic Nambe (38 K)
Dominic Nambe (38 K)
| Test: | Alma |
|---|
| Time: | 17:02 8 June 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 15 Mi. S of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 8,865 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 782 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 15.75 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 47.8 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 553 |
|---|
Free-fall LASL test of the Mk-59 using a Mk 39 Mod 0 Type 3 drop case. This test of the Mk-59 achieved a substantially higher yield than the Questa shot (which see for more information about the Mk-59). The device was similar to those tested in Questa, Rinconada, and Sunset. The achieved yield-to-weight ratio was 3.12 kt/kg. Caused some minor damage to buildings on the island.
| Test: | Truckee |
|---|
| Time: | 15:37 9 June 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 10 Mi. S of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 6,970 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 210 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 15.6 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 40.37 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 257 |
|---|
This was a parachute retarded LRL test of the XW-58 missile warhead in a Mk 36 drop case. This was a development and verification test for the Polaris A2 missile (which would carry three of these warheads). Satisfactory performance.
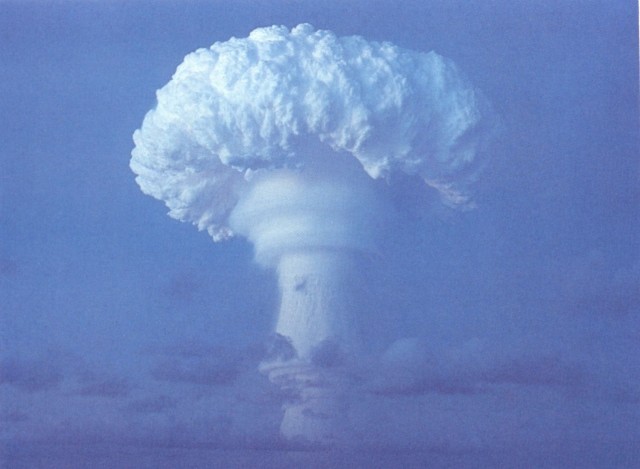 |
Dominic Truckee
|
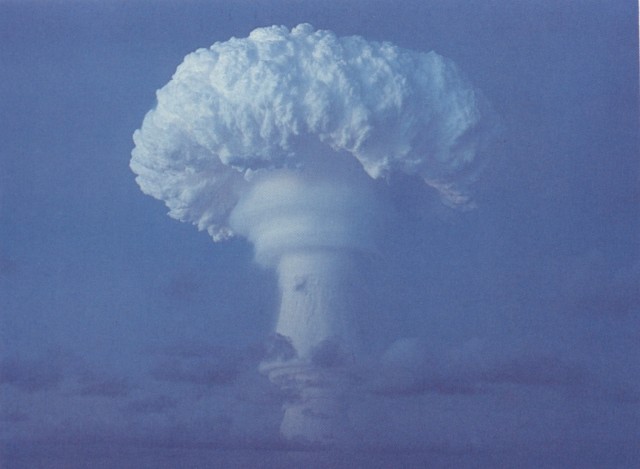 |
Dominic Truckee
|
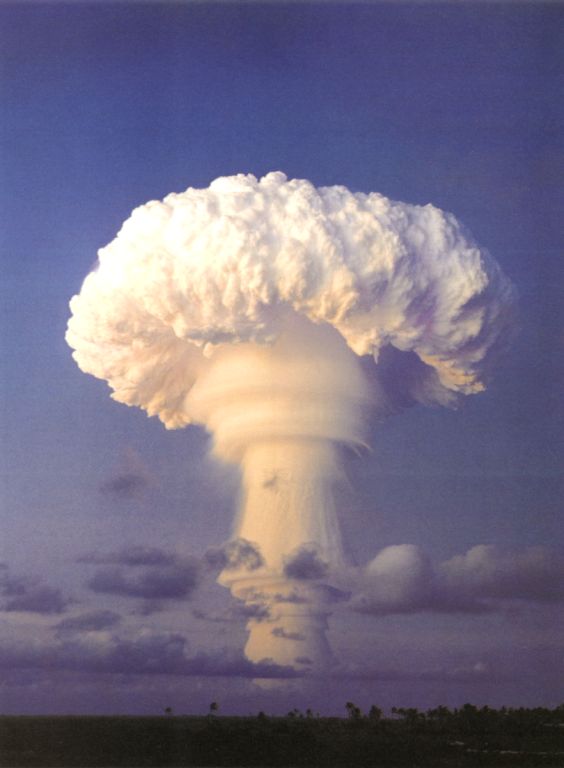 |
Dominic Truckee
|
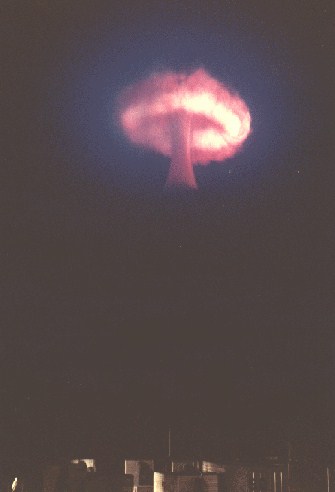 |
Dominic Truckee (20 K)
|
 |
Dominic Truckee (84 K)
|
| Test: | Yeso |
|---|
| Time: | 16:01 10 June 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 20 Mi. S of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 8,325 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 3000 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 27 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 48.3 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 1567 |
|---|
Free-fall LASL test of a device in a Mk 39 drop case. This was an advanced concepts test of the "16-M" device; similar to the Hardtack-I Koa test. The device performed as expected. This was the fourth largest Dominic explosion, and the largest to date in the series. The yield-to-weight ratio was 4.22 kt/kg.
 Dominic Yeso (34 K)
Dominic Yeso (34 K)
 Dominic Yeso (26 K)
Dominic Yeso (26 K)
| Test: | Harlem |
|---|
| Time: | 15:37 12 June 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 17 Mi. S of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 13,645 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 1200 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 18 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 46.6 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 773 |
|---|
Parachute-retarded LRL drop test of the W-47Y2 Polaris warhead in a Mk-36 drop case. This device used a Tuba thermonuclear secondary stage. The higher yield Y2 variant doubled the W-47Y1 yield, achieving a yield-to-weight ratio of 3.42 kt/kg.
| Test: | Rinconada |
|---|
| Time: | 16:00 15 June 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 17 Mi. S of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 9,105 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 800 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 15.75 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 39.83 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 507.4 |
|---|
A free-fall LASL airdrop of the XW-59 "Wall" device in a Mk-15 Mod 2 Type 3 drop case. This test successfully pushed the yield of the W-59 higher than previous tests, achieving a yield-to-weight ratio of 3.48 kt/kg. This device was similar to those tested in Questa, Alma, and Sunset. See Questa for more information on the W-59. The mushroom cloud rose to 65,000 feet.
| Test: | Dulce |
|---|
| Time: | 16:00 17 June 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | South of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 9,090 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 52 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 16.5 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 28.4 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | ? |
|---|
A free-fall LASL airdrop in a Mk-15 Mod 2 Type 3 drop case. The experimental light weight, high efficiency design was to similar to that tested in Mesilla (and thus was presumably also a Zippo I variant). The adequacy of the basic design was confirmed. The mushroom cloud rose to 58,000 feet.
| Test: | Petit |
|---|
| Time: | 15:01 19 June 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 17 Mi. S of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 14,995 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 2.2 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 24.41 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 63.29 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 498 |
|---|
A parachute-retarded LRL drop test of the Oboe device in a Mk 36 drop case. This was an advanced concepts test. It was a fizzle, the secondary stage did not ignite. This was the second fizzle of Dominic (the first being Tanana, also an LRL device). The mushroom cloud rose to 20-24,000 feet.
| Test: | Otowi |
|---|
| Time: | 16:00 22 June 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 10 Mi. S of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 9,010 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 81.5 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 15.4 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 42.7 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 166.1 |
|---|
LASL test of the Zippo-III device in a Mk-15 Mod 2 Type 3 drop case. An advanced concepts test of "novel system". The yield-to-weight ratio was 1.08 kt/kg (although new experimental designs are usually designed to produce good experimental data for future development, rather than to attempt maximum possible yields).
| Test: | Bighorn |
|---|
| Time: | 15:19 27 June 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 30 Mi. S of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 11,810 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 7650 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 45.65 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 96.18 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 4072.55 |
|---|
This was a test of the LRL Cello I-C device in a Mk-36 drop case. This was an advanced concepts test geared toward increasing thermonuclear yield-to-weight ratios. The test was successful, it produced the second largest yield of any Dominic shot and was the largest to date. The yield-to-weight ratio was 4.14 kt/kg. The mushroom cloud rose to 75,000 feet.
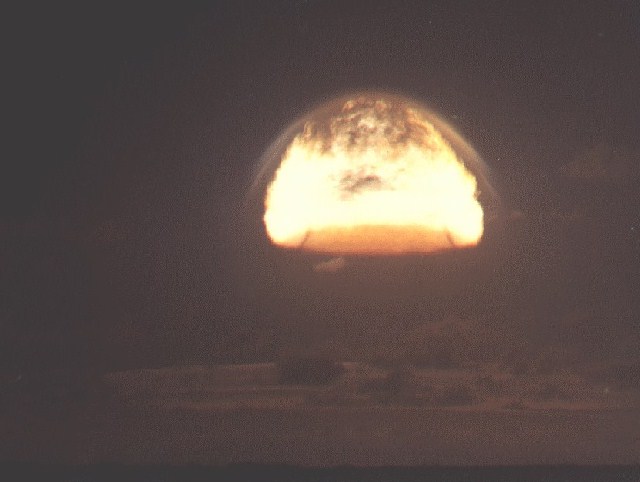 Dominic Bighorn (48 K)
Dominic Bighorn (48 K)
| Test: | Bluestone |
|---|
| Time: | 15:21 30 June 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 17 Mi. S of Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 4,980 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 1270 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 17.13 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 38 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 564.32 |
|---|
Bluestone was a parachute-retarded LRL test of the XW-56X2 Prime device in a Mk-36 drop case. The device was dropped by a new SAC crew on its first drop mission. The device was similar to that tested in Swanee and Arkansas (see Arkansas for more information about the W-56 warhead). This test was very successful, achieving the full design yield for the W-56 and an impressive 4.96 kt/kg yield-to-weight ratio, the highest known ratio demonstrated during Dominic. The mushroom cloud rose to 58,000 feet.
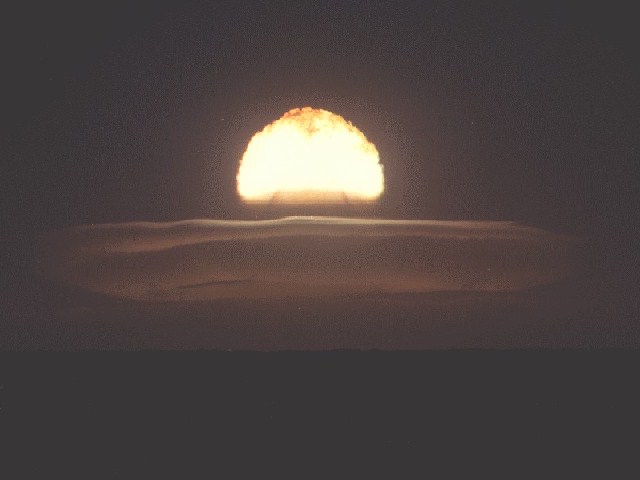 Dominic Bluestone (38 K)
Dominic Bluestone (38 K)
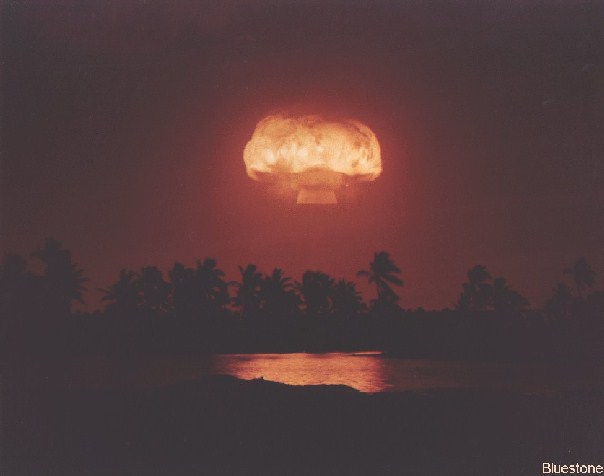 Dominic Bluestone (27 K)
Dominic Bluestone (27 K)
| Test: | Starfish Prime |
|---|
| Time: | 9:00 9 July 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | Johnston Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | Thor Missile Airburst; 248 miles |
|---|
| Yield: | 1450 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 20 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 54.3 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 1665 |
|---|
This was the second attempt to launch the Starfish test. The original Starfish was launched on 20 June, but the Thor missile engine cut out only 59 seconds after launch. The range safety officer sent the destruct signal 65 seconds after launch, and the missile was destroyed at 30-35,000 ft. The warhead high explosive detonated in 1-point safe fashion, destroying the warhead without producing nuclear yield. Large pieces of the missile fell back on Johnston Island, and more wreckage along with plutonium contamination was found on nearby Sand Island.
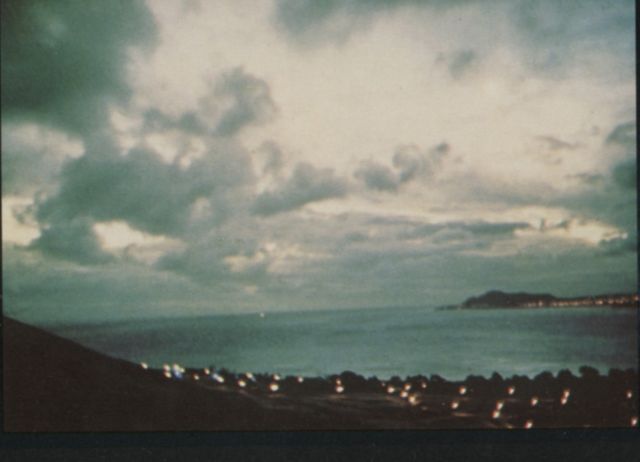
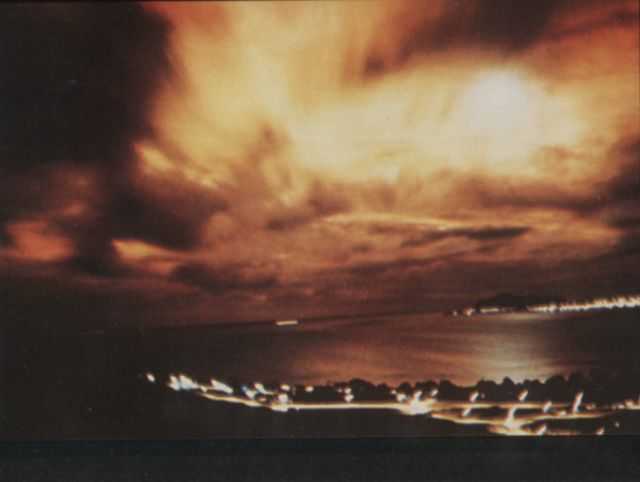
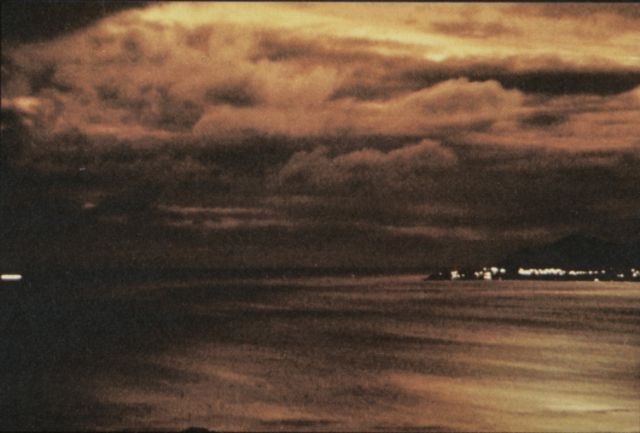
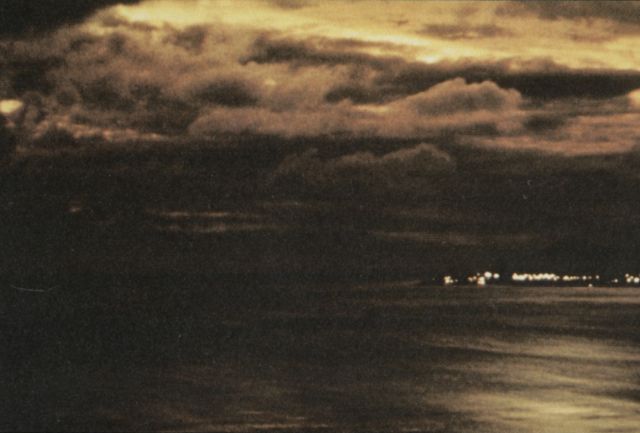
Starfish Prime was successful. The Thor missile carried the test instrumentation and the W-49 warhead/Mk-4 RV payload to 248 miles. The test appeared quite spectacular from Hawaii (800 miles away) and at Kwajalein (1600 miles away), with impressive light displays from an artifical aurora lasting up to seven minutes. The electromagnetic pulse (EMP) from this test sent power line surges throughout Oahu, knocking out street lighting, blowing fuzes and circuit breakers, and triggering burglar alarms.
The W-49 warhead used in this test was used on the Thor, Atlas, Jupiter, and Titan missiles, and was a descendant of the versatile Mk-28 thermonuclear bomb.
| Starfish Prime as seen from Honolulu |
|---|
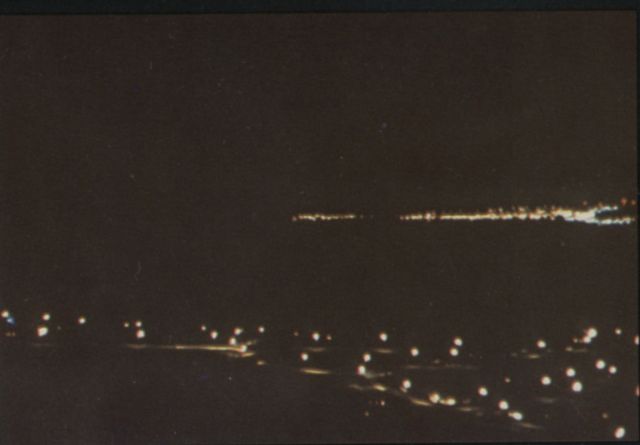 |
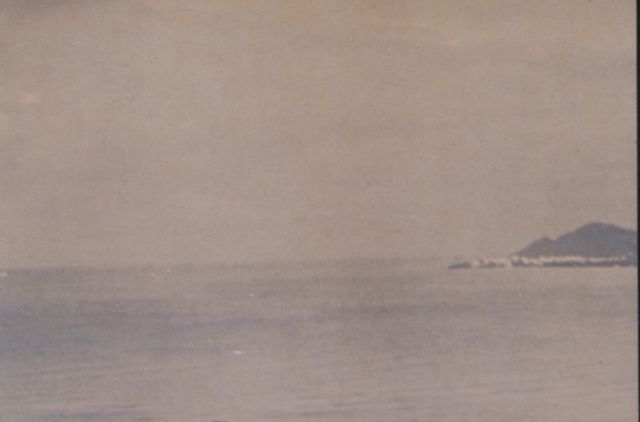 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
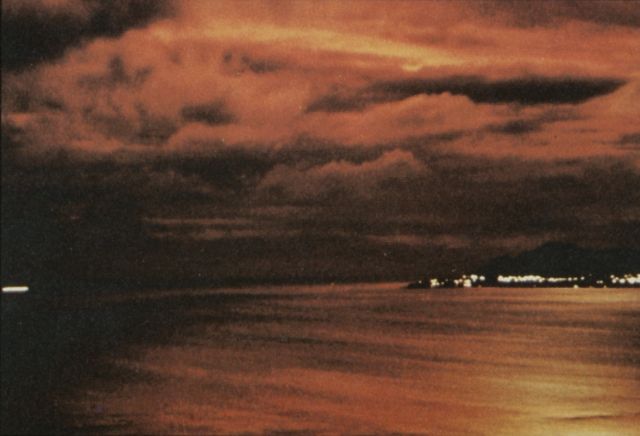 |
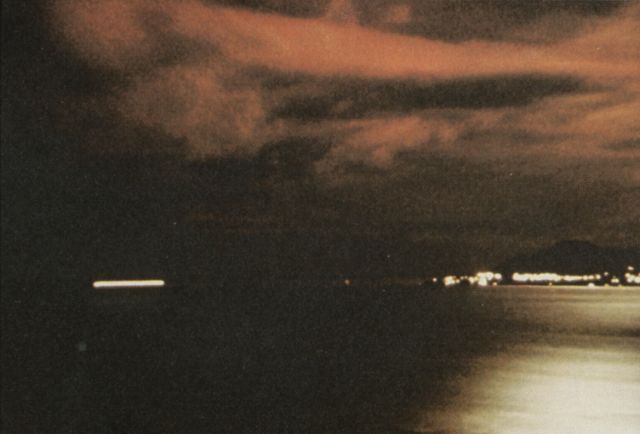 |
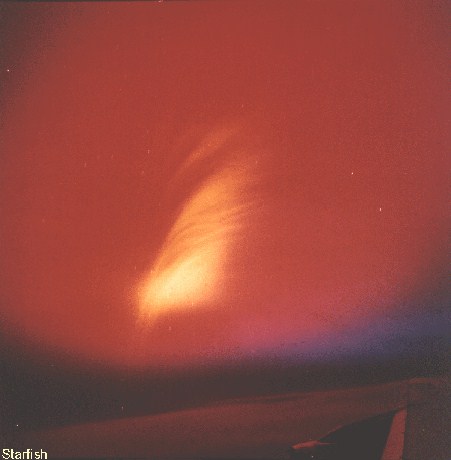 Dominic Starfish Prime (30 K)
Dominic Starfish Prime (30 K)
 Dominic Starfish Prime (23 K)
Dominic Starfish Prime (23 K)
| Test: | Sunset |
|---|
| Time: | 16:33 10 July 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 5,000 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 1000 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 15.75 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 39.83 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 543 |
|---|
High yield test of the LASL XW-59 warhead in a Mk-15 Mod 2 Type 3 drop case. This test successfully reached the full design yield of the W-59, with a yield-to-weight ratio of 4.06 kt/kg. This device was similar to those tested in Questa, Alma, and Rinconada. See Questa for more information on the W-59. The mushroom cloud rose to over 60,000 feet.
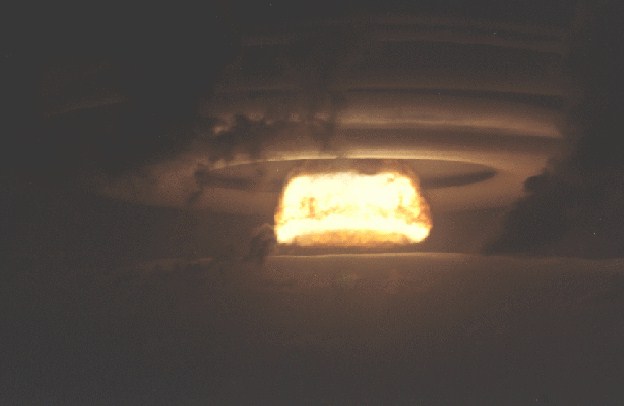 Dominic Sunset (29 K)
Dominic Sunset (29 K)
| Test: | Pamlico |
|---|
| Time: | 15:37 11 July 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | Christmas Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 14,330 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 3880 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 56.2 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 123.4 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 9161.67 |
|---|
A parachute-retarded LRL device in a MK-36 drop case. This was a test of advanced principles for achieving high-efficiency thermonuclear burn, and successfully confirmed theoretical predictions. It was said to "show the way to a new range of possibilities in high-yield design". This was the last Christmas Island airdrop, and the third largest test of Operation Dominic. Yield-to-weight ratio was 0.934 kt/kg (but then this was an experiment, not a final weapon configuration).
| Test: | Androscoggin |
|---|
| Time: | 16:17 2 October 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 250 Mi. SSW of Johnston Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 10,260 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 75 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 56.2 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 128.5 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 6647.52 |
|---|
This LRL shot, intended to be a high yield design test, was a fizzle. The device tested was possibly a Ripple device. This was the first U.S. test were all of the test instrumentation was carried on aircraft. RC-121, C-130, KC-135, and AFSWC RB-52B aircraft were used. These same aircraft were used on all five Johnston Island airdrop tests. This shot was later retested successfully in Housatonic (yield 8.3 Mt). The mushroom cloud rose to 54,000 feet.
| Test: | Bumping |
|---|
| Time: | 16:02 6 October 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | Johnston Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 10,000 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 11.3 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 39.37 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 78.43 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 1155 |
|---|
This LRL shot was a retest of the Oboe device fired in Dominic Petit, which was a fizzle (2.2 kt). It was dropped in a Mk-36 drop case. This was an advanced concepts test to improve warhead yield-to-weight ratio. The yield much lower than expected. The mushroom rose to 50,000 ft.
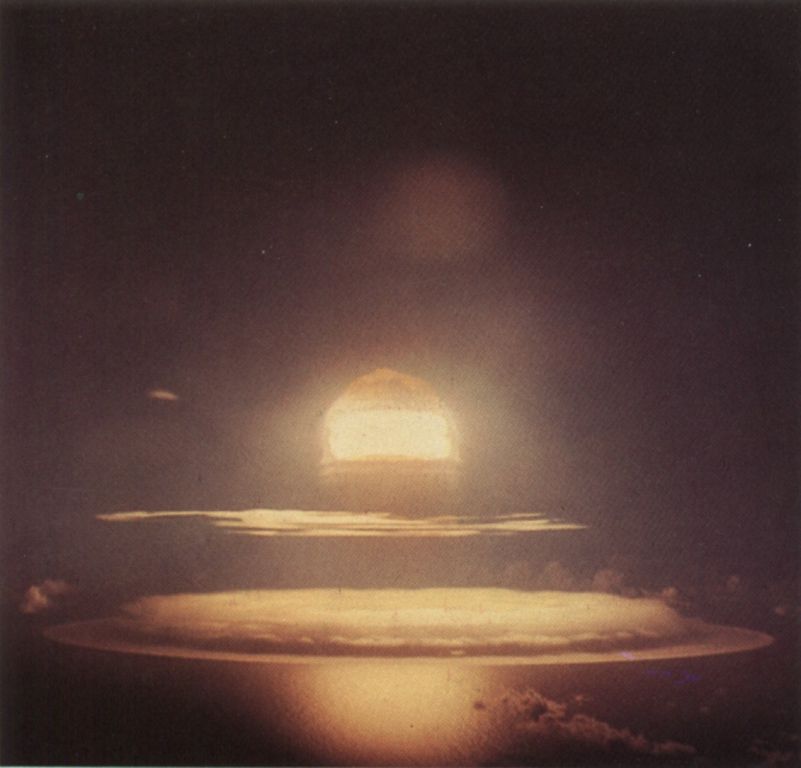
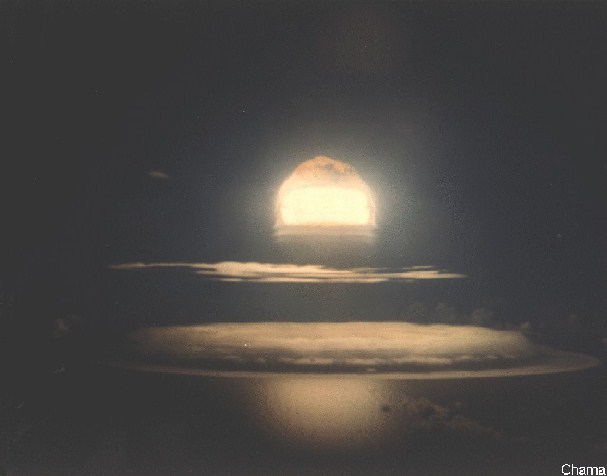
| Test: | Chama |
|---|
| Time: | 16:01 18 October 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | Johnston Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 11,970 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 1590 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 27.98 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 89 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 2350 |
|---|
This was a free-fall LASL test of the Thumbelina device in a Mk-36 drop case. This was a test of a light weight small diameter device, possibly a replacement for the W-38 (the 2-4 Mt warhead for the Atlas and Titan I missiles). The results are variously described as "thoroughly successful" while the yield was reported to be below the predicted value.
| Test: | Checkmate |
|---|
| Time: | 8:30 20 October 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 43 Mi. from Johnston Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | Missile Airburst; 483,000 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | Low kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 14 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 20 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 150 |
|---|
This was the second successful Operation Fishbowl shot. This was a test of the LASL XW-50X1 warhead launched by a solid fueled XM-33 Strypi rocket using an Army Recruit rocket booster stage. The warhead detonated at an altitude of 91.3 miles, 41 miles downrange from Johnston Island, and only 3 kilometers from the airzero point. See Adobe for more information about the W-50 warhead. This was possibly the lowest yield variant, the Y1, with a yield of 60 kt.
Since the shot occurred essentialy above the atmosphere, a luminous fireball was not formed. Instead observers on the island at the moment of detoantion saw a green and blue circular region surrounded by a blood red ring. This faded in less than a minute, and blue-green streamers and pink striations developed that lasted half an hour.
| Test: | Bluegill Triple Prime |
|---|
| Time: | 9:59 26 October 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 19 Mi. SSW of Johnston Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | Thor Missile Airburst; 160,000 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | <1000 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 14 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 44 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 409 |
|---|
Bluegill Triple Prime was the fourth attempt to launch this high altitude test, originally slated to be the first Operation Fishbowl shot. The Bluegill experiment used a W-50 warhead in a Mk 4 RV, launched by a Thor missile. The device was similar to those fired in Adobe (which see for more information on the W-50), Aztec, and Kingfish. This was possibly the 200 kt Y2 or the 400 kt Y3 W-50 variant.
The initial attempt (Bluegill) was launched at midnight (local time) on 3 June. Problems had been encountered with the range safety radar prior to launch, and five minutes after launch the Johnston Island missile tracking system failed. Unable to monitor the missile's flight path, the range safety officer destroyed it 10 minutes later, prior to warhead detonation.
The second attempt (Bluegill Prime) at 23:15 (local) on 25 July was a genuine disaster. The Thor missile was carrying one pod, two re-entry vehicles (all heavily instrumented) and the warhead. The missile engine malfunctioned immediately after ignition, and the range safety officer fired the destruct system, whille the missile was still on the launch pad. The Johnston Island launch complex was demolished, and heavily contaminated with plutonium. Complete reconstruction was required before launches could be resumed.
The third attempt (Bluegill Double Prime) was made at 21:14 on 15 October (local). The missile was launched on a true bearing of 150 degrees. Between 86 and 90 seconds in to the flight booster failure occurred and the missile began tumbling, the missile was destroyed by remote control 156 seconds after launch. Some radioactive debris fell back on to Johnston Island.
The fourth and finally successful launch resulted in a detonation at an altitude of 31 miles, approximately 19 miles south-southwest of Johnston Island. This burst occurred low enough in the atmosphere for fireball formation to occur, and observers saw a brilliant white flash and noticeable heat pulse on bare skin. A slightly distorted bright moon-like sphere was seen, yellow at first, then gradually showing green, pink, and violet hues. Blue-purple streamers were formed. A bright glow persisted for 30 minutes, at times bright enough to read a watch face in the dark. The fireball was seen in Hawaii also.
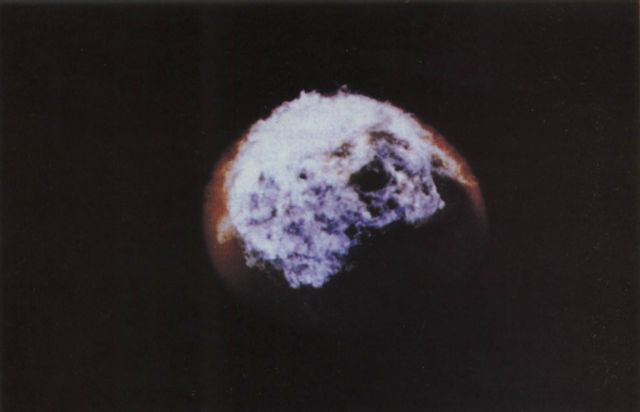 |
Fishbowl Bluegill Triple Prime
|
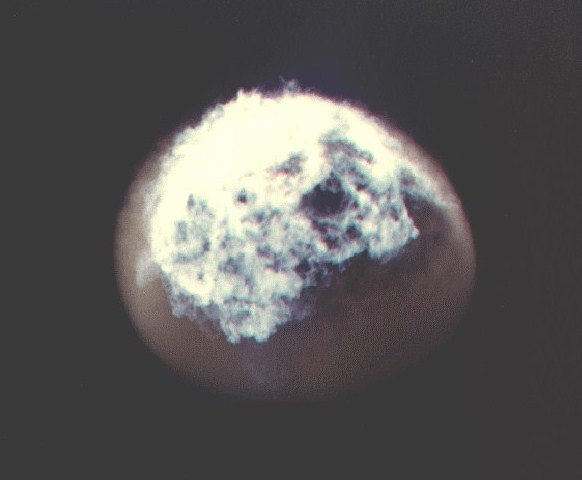 |
Fishbowl Bluegill Triple Prime (31 K)
|
| Test: | Calamity |
|---|
| Time: | 15:46 27-Oct-62 |
|---|
| Location: | Johnston Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 11,780 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 800 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 34.4 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 93 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 1830 |
|---|
An LRL airdrop using a Mk-15 drop case. Said to be the third drop test of a specific device to maximize yield to weight ratio (demonstrated ratio was 0.96 kt/kg). The bombing error was less than 500 feet, and all diagnostic and effects aircraft obtained excellent data. The mushroom cloud rose to 63,000 feet.
| Test: | Housatonic |
|---|
| Time: | 16:01 30 October 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | Johnston Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | B-52 Airdrop; 12,130 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | 8300 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 56.2 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 147.9 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 7139.55 |
|---|
This LRL airdrop was the final nuclear weapon airdrop by the U.S. The device tested was a Ripple II in a Mk-36 drop case, and it was delivered with near-perfect accuracy (bombing error less than 100 feet). This was a repeat of the failed Androscoggin and was spectacularly successful, resulting in the highest yield of the Dominic test series. The yield-to-weight ratio was 2.56 kt/kg.
| Test: | Kingfish |
|---|
| Time: | 12:10 1 November 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 43 Mi. SSW of Johnston Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | Thor Missile Airburst; 320,000 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | <1000 kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 15.4 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 44 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 409 |
|---|
This was the fourth successful Fishbowl test. The system that was fired was similar to Bluegill Triple Prime, a W-50 in Mk 4 RV launched by a Thor missile. The W-50 was also used in Adobe (which see for more information on the W-50) and Aztec. This was possibly the 200 kt Y2 or the 400 kt Y3 W-50 variant.
The detonation occurred at an altitude of 60 miles. The dramatic visual (and other) effects were observed over much of the central Pacific. The explosion appeared as a bright yellow glow, at first circular, but elongating along a south-to-northwest axis. The long axis reached 125 miles after 30 minutes, and eventually reached 185 miles. The glow persisted for at least 1.5 hours. On Johnston Island a yellow-white luminous circle with intense purple streamers was visible for the first minute. Brilliant streamers (beta particle auroras) were seen going north and south from Maui. At Oahu a bright flash was seen, and after about ten seconds a great white ball was seen rising slowly out of the sea and remained visible for several minutes.
Another major effect of this shot was the widespread disturbance of the ionosphere and the consequent disruption of radio communications over the central Pacific, which lasted at least three hours.
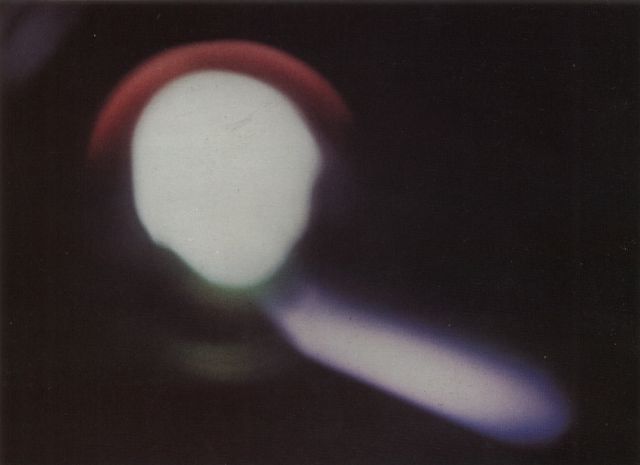 |
Fishbowl Kingfish
|
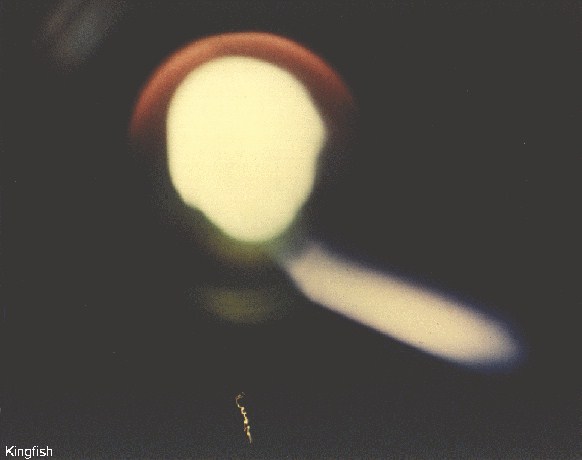 |
Fishbowl Kingfish (28 K)
|
| Test: | Tightrope |
|---|
| Time: | 0:00 4 November 1962 (GMT) |
|---|
| Location: | 2 Mi. SSW of Johnston Island |
|---|
| Test Height and Type: | Nike Hercules Missile Airburst; 69,000 Feet |
|---|
| Yield: | Low kt |
|---|
| Device Diameter (inches): | 29 |
|---|
| Device Length (inches): | 39.3 |
|---|
| Device Weight (lb.): | 900 |
|---|
This was a DOD sponsored live test of the Nike Hercules air defense missile system. A Nike Hercules missile, carrying the LASL designed W-31 air defense warhead, was launched and detonated over Johnston Island. The W-31 came in four yield variants ranging from 1 to 40 kt, it is not known which was fired in this test.
On Johnston Island an intense white flash, to bright to view even through high density goggles, was accompanied by a strong heat pulse. A yellow-orange disc formed, slowly changing to a purple toroid which faded from view after several minutes.
This shot is usually regarded as the last U.S. atmospheric test. The later zero-yield atmospheric plutonium dispersal tests conducted in Operation Roller Coaster are however listed as "nuclear tests" by the U.S. government and counted as part of the total of U.S. nuclear tests. Furthermore, several later Plowshare nuclear tests (Cabriolet, Palanquin, Buggy, and Schooner) were surface cratering shots, in which the explosions intentionally broke through the surface, venting a substantial fraction of the radioactivity produced.
 |
Fishbowl Tightrope
|
Operation Dominic Summary
Legend:WD=Weapons Development, WE=Weapons Effects, ST=Safety Test, TN= Thermonuclear, LASL=Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory, UCRL=University of California Radiation Laboratory (later Lawrence Livermore), DOD = Department of Defense.
| Test Name |
Time and Date (GMT) |
Location |
Test Type |
Height (Ft) |
Yield (kt) |
Sponsor |
Purpose |
Comments |
| Adobe |
15:45 25-Apr-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
2,900 |
190 |
LASL |
WD |
XW-50X1-Y2 verification test, sim. to Aztec, Kingfish, Bluegill Triple Prime |
| Aztec |
16:01 27-Apr-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
2,610 |
410 |
LASL |
WD |
XW-50X1-Y3 test, sim. to Adobe, Kingfish, Bluegill Triple Prime, yield slightly lower than expected |
| Arkansas |
18:00.00.16 27-Apr-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
5,030 |
1090 |
LRL |
WD |
XW-56X2 test, highly successful, used Fife secondary stage |
| Questa |
18:01 2-May-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
5,230 |
670 |
LASL |
WD |
XW-59 test, sim. to Alma, Rinconada, Sunset, yield considerably lower than expected |
| Frigate Bird |
23:30 6-May-62 |
Johnston Island |
SLBM Airburst |
11,000 |
600 |
LRL |
WD |
Only US operational ballistic missile launch w/live warhead, Polaris SLBM/W-47Y1/Mk-1 RV combo, successful |
| Yukon |
18:01 8-May-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
2,880 |
100 |
LRL |
WD |
Calliope II device, 1st test of high fusion/low fission family; sim. to Muskegon, Chetco, Nougat Arikaree, Hudson, Codsaw, Hoosic; yield slightly higher than expected |
| Mesilla |
17:01 9-May-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
2,450 |
100 |
LASL |
WD |
Zippo-I device, advanced primary & secondary concepts test, yield considerably lower than expected |
| Muskegon |
15:37 11-May-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
2,995 |
50 |
LRL |
WD |
Calliope IV device, advanced lightweight low fission concept, sim. to Chetco and Yukon, slightly lower than expected yield |
| Swordfish |
20:02 11-May-62 |
400 nm W San Diego |
Underwater |
-650 |
<20 |
LASL |
WD |
Full scale ASROC/W-44 ASW rocket proof test, sim. to Nougat Chena |
| Encino |
17:02 12-May-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
5,510 |
500 |
LASL |
WD |
XW-43Y5 warhead, verification of reduced yield variant of HT-I Elder shot |
| Swanee |
15:21 14-May-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
2,940 |
97 |
LRL |
WD |
XW-56 "clean" ABM warhead test, sim. to Bluestone, possible W-65 progenitor, highly experimental, yield lower than expected |
| Chetco |
15:36 19-May-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
6,905 |
73 |
LRL |
WD |
Calliope I device, advanced light weight concept, sim. to Muskegon and Yukon, yield close to predicted |
| Tanana |
16:08 25-May-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
9,030 |
2.6 |
LRL |
WD |
Calliope III device fizzle, "radical" design |
| Nambe |
17:02 27-May-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
7,140 |
43 |
LASL |
WD |
Zippo-II device, "unique" design, advanced concepts test, yield lower than expected |
| Alma |
17:02 8-Jun-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
8,865 |
782 |
LASL |
WD |
Mk-59, sim. to Questa, Rinconada, Sunset |
| Truckee |
15:37 9-Jun-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
6,970 |
210 |
LRL |
WD |
XW-58, development and verification test, satisfactory |
| Yeso |
16:01 10-Jun-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
8,325 |
3000 |
LASL |
WD |
Advanced concepts test of "16-M" device, sim. to HT-I Koa, performed as expected |
| Harlem |
15:37 12-Jun-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
13,645 |
1200 |
LRL |
WD |
W-47Y2 test, Tuba secondary, successful, doubled W-47Y1 yield |
| Rinconada |
16:00 15-Jun-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
9,105 |
800 |
LASL |
WD |
XW-59 "Wall" device, increased yield warhead test, successful, sim. to Questa, Alma, Sunset |
| Dulce |
16:00 17-Jun-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
9,090 |
52 |
LASL |
WD |
Experimental lightweight, high efficiency design, sim to Mesilla, basic design adequacy confirmed |
| Petit |
15:01 19-Jun-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
14,995 |
2.2 |
LRL |
WD |
Oboe device, advanced concepts test, second LRL fizzle |
| Otowi |
16:00 22-Jun-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
9,010 |
81.5 |
LASL |
WD |
Zippo-III device, advanced concepts test of "novel system" |
| Bighorn |
15:19 27-Jun-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
11,810 |
7650 |
LRL |
WD |
Cello I-C device, advanced concepts test, successful |
| Bluestone |
15:21 30-Jun-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
4,980 |
1270 |
LRL |
WD |
XW-56X2 Prime test, sim. to Swanee |
| Starfish Prime |
9:00 9-Jul-62 |
Johnston Island |
Missile Airburst |
248 miles |
1450 |
LASL |
WE |
High altitude effects test, W-49 warhead/Mk-4 RV on Thor missile |
| Sunset |
16:33 10-Jul-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
5,000 |
1000 |
LASL |
WD |
High yield XW-59 advanced concepts test, sim. to Questa, Alma, Rinconada |
| Pamlico |
15:37 11-Jul-62 |
Christmas Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
14,330 |
3880 |
LRL |
WD |
Advanced principles test for high-efficiency TN burn, successful, last Christmas Island airdrop |
| Androscoggin |
16:17 2-Oct-62 |
Johnston Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
10,260 |
75 |
LRL |
WD |
Possible Ripple device, fizzle, retested in Housatonic shot |
| Bumping |
16:02 6-Oct-62 |
Johnston Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
10,000 |
11.3 |
LRL |
WD |
Possible Oboe device, retest of Petit, yield much lower than expected, test to improve yield-to-weight ratio |
| Chama |
16:01 18-Oct-62 |
Johnston Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
11,970 |
1590 |
LASL |
WD |
Thumbelina device, test of lightweight small diameter device, possible replacement for W-38, yield below predicted value |
| Checkmate |
8:30 20-Oct-62 |
Johnston Island |
Missile Airburst |
483,000 |
Low |
LASL |
WE |
XW-50X1 warhead high altitude effects shot |
| Bluegill Triple Prime |
9:59 26-Oct-62 |
Johnston Island |
Missile Airburst |
160,000 |
<1000 |
LASL |
WE |
W-50 in Mk 4 RV, Thor missile launched, sim. to Adobe, Aztec, Kingfish |
| Calamity |
15:46 27-Oct-97 |
Johnston Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
11,780 |
800 |
LRL |
WD |
Third drop test of specific device to maximize yield to weight ratio |
| Housatonic |
16:01 30-Oct-62 |
Johnston Island |
B-52 Airdrop |
12,130 |
8300 |
LRL |
WD |
Ripple II device, repeat of Androscoggin, successful, last U.S. nuclear weapon airdrop |
| Kingfish |
12:10 1-Nov-62 |
Johnston Island |
Missile Airburst |
320,000 |
<1000 |
LASL |
WE |
W-50 in Mk 4 RV, Thor missile launched, sim. to Adobe, Aztec, Bluegill Triple Prime |
| Tightrope |
0:00 4-Nov-62 |
Johnston Island |
Missile Airburst |
69,000 |
Low |
LASL |
WE |
W-31 air defense warhead on Nike Hercules missile, last U.S. atmospheric test, successful |







 Dominic Aztec (34 K)
Dominic Aztec (34 K)
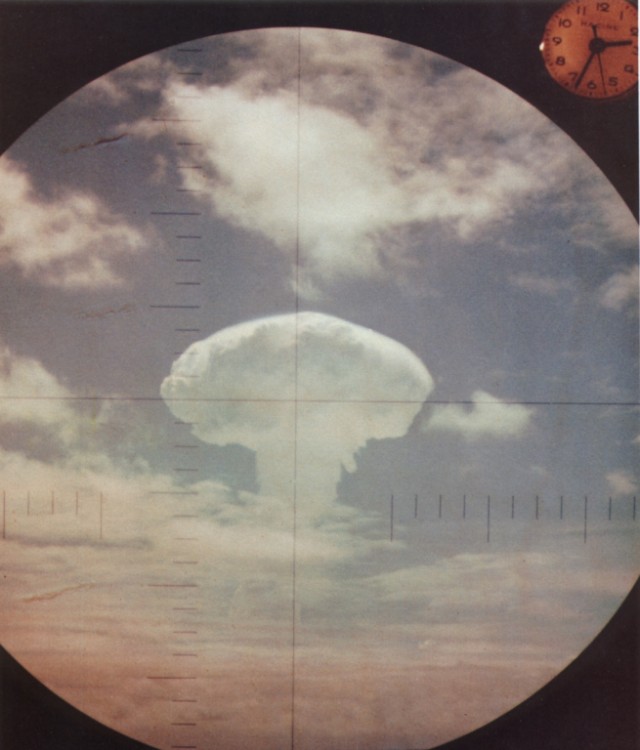










 Dominic Swordfish launch (26 K)
Dominic Swordfish launch (26 K) Dominic Swordfish spray dome (25 K)
Dominic Swordfish spray dome (25 K) Dominic Swordfish spray dome dispersing(28 K)
Dominic Swordfish spray dome dispersing(28 K) Swordfish spray dome dispersing further(80 K)
Swordfish spray dome dispersing further(80 K) Swordfish spray dome from above (53 K)
Swordfish spray dome from above (53 K)

























